In an irrotational spacetime, Eq. (46) becomes
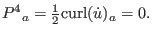 |
(75) |
It introduces a scalar potential:
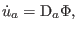 |
(76) |
where  is the acceleration potential. This scalar potential
corresponds to the Newtonian potential. In the irrotational
Newtonian model, the linearized acceleration is characterized as the
acceleration potential.
is the acceleration potential. This scalar potential
corresponds to the Newtonian potential. In the irrotational
Newtonian model, the linearized acceleration is characterized as the
acceleration potential.
Ashkbiz Danehkar
2018-03-26